Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, continues to be a significant health concern in the United States and globally. Despite advancements in medical knowledge and treatment options, uncontrolled hypertension remains a persistent threat to public health, earning its reputation as the "silent killer." This article delves into the current state of hypertension management, its impact on cardiovascular health, and the challenges faced by healthcare providers and patients in effectively controlling this condition.
The Prevalence of Hypertension
Hypertension affects a staggering 45% of the adult population in the United States[2]. This high prevalence underscores the importance of understanding and addressing this condition. To put this into perspective:
- Nearly half of all American adults are living with hypertension
- Many individuals are unaware of their condition due to its often asymptomatic nature
- Uncontrolled hypertension significantly increases the risk of serious health complications
The widespread nature of hypertension makes it a critical public health issue that demands attention from both healthcare providers and the general public.
Understanding Hypertension
What is hypertension?
Hypertension is a chronic medical condition characterized by persistently elevated blood pressure in the arteries. Blood pressure is measured using two values:
- Systolic pressure: The pressure in the arteries when the heart contracts
- Diastolic pressure: The pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest between beats
According to the latest guidelines from the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology, healthy individuals should maintain:
- Systolic blood pressure of 130 millimeters of mercury (mmHg) or less
- Diastolic blood pressure of 80 mmHg or less[2]
The dangers of uncontrolled hypertension
Uncontrolled hypertension is a major risk factor for several life-threatening conditions:
- Stroke
- Heart attacks
- Kidney disease
- Sudden cardiac death
In fact, cardiovascular disease, primarily heart attacks and strokes, accounts for more than 900,000 annual deaths in the United States and about 10 million deaths globally[2]. These statistics highlight the urgent need for better hypertension management and control.
The Current State of Hypertension Awareness and Treatment
While progress has been made in hypertension awareness and treatment since the 1970s, there is still significant room for improvement. Current statistics show:
- 54% of individuals with hypertension are aware of their condition
- 40% are actively treated
- Only 21% have their hypertension effectively controlled[2]
These figures represent an improvement from the 1970s when only about 50% of patients were aware of their hypertension, and even fewer received effective treatment. However, they also indicate that a large portion of the population remains at risk due to uncontrolled hypertension.
Challenges in Hypertension Management
Variability in blood pressure readings
One of the challenges in managing hypertension is the natural variability of blood pressure. Blood pressure can fluctuate:
- From day to day
- Throughout the day (morning to night)
- Based on various factors such as stress, physical activity, and diet
This variability makes it crucial for healthcare providers to develop personalized treatment algorithms for each patient and for patients to take an active role in monitoring their blood pressure.
The role of metabolic syndrome
Another clinical challenge in hypertension management is metabolic syndrome, which includes:
- Central adiposity (excess abdominal fat)
- High triglycerides
- Low high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol
- Elevated fasting blood glucose
- Hypertension
Metabolic syndrome is a significant risk factor for heart attacks and stroke, particularly in the United States, which has one of the highest obesity rates globally[2].
Effective Strategies for Hypertension Management
Lifestyle modifications
Making positive lifestyle changes is crucial in managing hypertension. These changes include:
- Weight loss: Reducing excess body weight can significantly lower blood pressure
- Increased physical activity: Regular exercise helps improve cardiovascular health
- Reduced salt intake: Limiting sodium consumption can help lower blood pressure
- Healthy diet: Adopting a balanced, nutrient-rich diet supports overall heart health
Medication management
For individuals whose blood pressure remains above 140/90 mmHg despite lifestyle changes, medication may be necessary. Some effective medication options include:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
- Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs)
- Diuretics
- Calcium channel blockers
- Beta-blockers
The choice of medication depends on individual patient factors and should be determined by a healthcare provider.
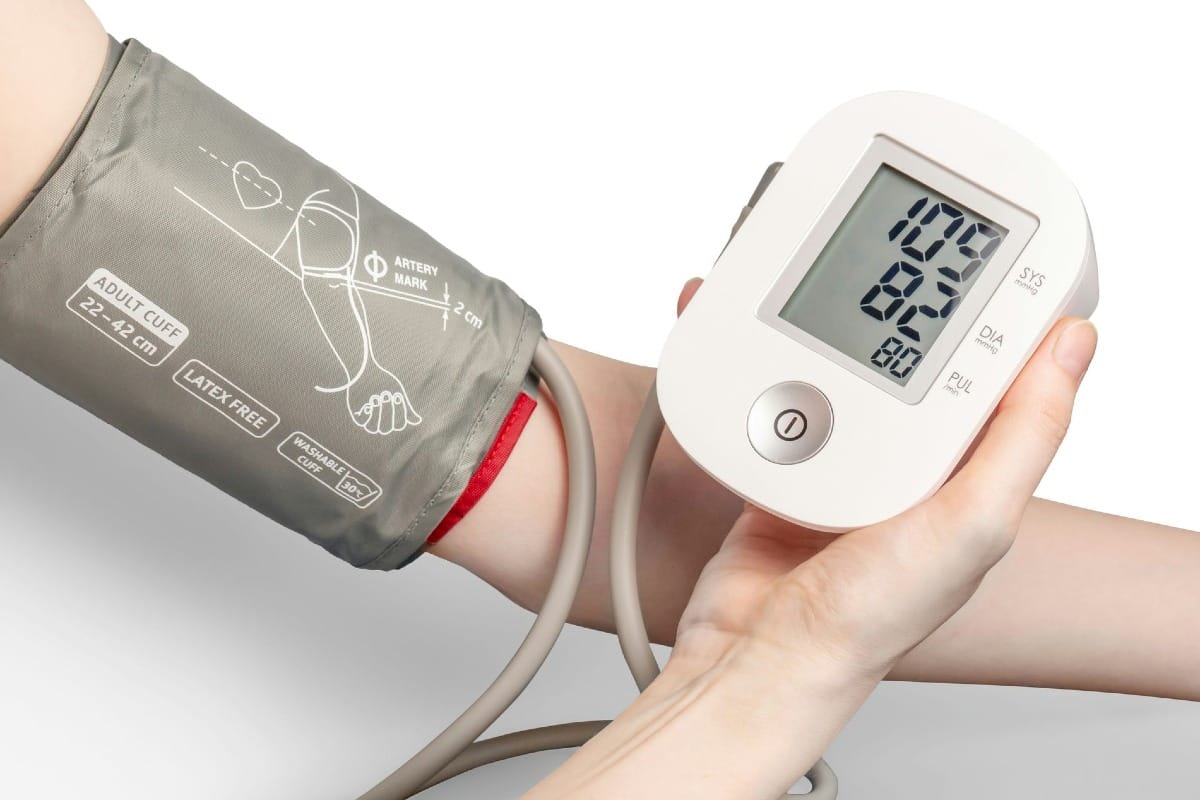
The Importance of Home Blood Pressure Monitoring
Regular monitoring of blood pressure at home is crucial for effective hypertension management. The American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology recommend:
- Using a reliable home blood pressure monitor, such as the Omron device
- Checking blood pressure each morning and night
- Taking the average of three readings, about five minutes apart, for each measurement[2]
Home monitoring allows patients to:
- Track their blood pressure trends over time
- Identify fluctuations that may require medication adjustments
- Actively participate in their hypertension management
The Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a critical role in addressing the challenge of uncontrolled hypertension. They should:
- Regularly screen patients for hypertension
- Educate patients about the risks of uncontrolled hypertension
- Develop personalized treatment plans
- Monitor treatment effectiveness and make adjustments as needed
- Encourage patient engagement in self-monitoring and lifestyle modifications
Future Directions in Hypertension Management
As research in hypertension management continues, several areas show promise for improving outcomes:
- Personalized medicine approaches based on genetic and environmental factors
- Advanced technologies for continuous blood pressure monitoring
- Development of new medications with fewer side effects
- Improved strategies for patient education and engagement
- Integration of artificial intelligence in hypertension management and risk prediction
Conclusion
Uncontrolled hypertension remains a significant health challenge, despite advances in medical knowledge and treatment options. The persistence of this "silent killer" underscores the need for continued efforts in hypertension awareness, prevention, and management.
By combining lifestyle modifications, appropriate medication use, regular monitoring, and active engagement between patients and healthcare providers, it is possible to improve hypertension control rates and reduce the risk of associated cardiovascular complications.
As we move forward, it is crucial for both healthcare providers and patients to remain vigilant in the fight against hypertension. By doing so, we can work towards "killing the old silent killer" and improving cardiovascular health outcomes for millions of individuals worldwide.
Citations: [1] https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2024/08/240801121838.htm











Member discussion