Wearable technology is revolutionizing personalized health tracking by providing real-time insights into various health metrics, from heart rate and sleep patterns to stress levels and blood glucose monitoring. As these devices become more advanced, they empower individuals to take proactive control of their wellness, offering tailored recommendations and seamless integration with healthcare systems for improved health outcomes.
Evolution of Wearable Health Tech
Wearable health technology has undergone a significant transformation since its inception, evolving from basic fitness trackers to sophisticated devices capable of monitoring a wide range of health metrics. Early wearables primarily focused on tracking physical activity, such as steps taken and calories burned. However, advancements in sensor technology, artificial intelligence (AI), and data analytics have expanded their capabilities substantially.
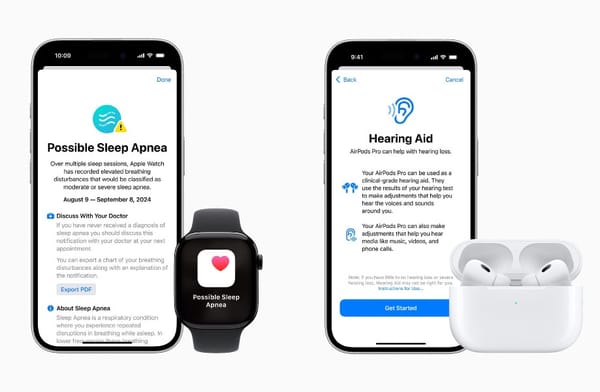
Modern wearable devices now include features such as continuous glucose monitoring, electrocardiograms (ECG), and blood pressure tracking, providing users with comprehensive health insights. These devices leverage AI to analyze collected data, offering personalized health recommendations and predictive analytics that can detect potential health issues before they become critical[1][2][3].
The integration of wearable technology with healthcare systems has also advanced, enabling real-time data sharing with healthcare providers. This facilitates remote patient monitoring, particularly beneficial for managing chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases. By providing continuous health tracking, wearables help in early detection of health anomalies, thereby improving preventive care and reducing hospital readmissions[1][2][3].
In addition to medical-grade wearables, consumer-grade devices have gained popularity due to their accessibility and ease of use. These devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, often include features like stress monitoring, sleep quality analysis, and hydration tracking. They empower users to take an active role in managing their health and wellness by providing actionable insights and personalized fitness plans[1][2][3][4].
The future of wearable health technology looks promising, with ongoing research and development focusing on integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar and kinetic energy, to enhance battery life and device sustainability. Innovations like smart clothing embedded with sensors and augmented reality (AR) glasses are also on the horizon, offering new ways to monitor and improve health[1][2][3][4].
However, the evolution of wearable health tech is not without challenges. Issues such as data privacy, sensor accuracy, and the digital divide must be addressed to ensure these technologies are both effective and accessible to all users. As wearable technology continues to advance, it holds the potential to revolutionize personalized health tracking and wellness management, making proactive healthcare more attainable for everyone[1][2][3][4][5].
Sources:
AI in Wearable Devices
Artificial intelligence (AI) is significantly enhancing the functionality and impact of wearable devices in healthcare. AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of data collected by wearables, providing personalized insights and predictive analytics that can transform patient care. For instance, AI-powered wearables can monitor vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels, offering real-time feedback and early warnings about potential health issues[1][2][3].
One of the key applications of AI in wearables is in chronic disease management. Devices equipped with AI can continuously track health metrics and detect anomalies, prompting timely interventions. This is particularly beneficial for managing conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases, where continuous monitoring is crucial[1][2]. AI algorithms can predict potential health events, such as heart attacks or hypoglycemic episodes, allowing for preventive measures to be taken before the situation becomes critical[2][3].
AI also enhances the user experience by providing personalized health recommendations. For example, fitness trackers and smartwatches use AI to analyze users' activity levels, sleep patterns, and other health data to offer tailored fitness plans and wellness tips. This personalized approach helps users set realistic goals and stay motivated, ultimately leading to better health outcomes[2][3][4].
Moreover, AI integration in wearables facilitates remote patient monitoring, enabling healthcare providers to keep track of patients' health outside clinical settings. This is particularly useful for elderly patients or those with mobility issues, as it reduces the need for frequent hospital visits and allows for continuous care from the comfort of their homes[1][2]. AI-driven wearables can also alert healthcare providers to any significant changes in a patient's condition, ensuring timely medical intervention[1][2].
Despite these advancements, the integration of AI in wearable devices faces several challenges. Data privacy and security are major concerns, as wearables collect sensitive health information that must be protected from unauthorized access. Additionally, the accuracy and reliability of AI algorithms depend on the quality of the data collected by the sensors, which can vary between different devices and manufacturers[1][2][3]. Addressing these challenges is essential to fully leverage the potential of AI in wearable technology.
In conclusion, AI is revolutionizing wearable devices by providing advanced health monitoring, personalized insights, and predictive analytics. These capabilities not only enhance individual health management but also improve the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare delivery[1][2][3][4]. As AI technology continues to evolve, its integration with wearables will likely lead to even more innovative solutions for personalized health and wellness.
Sources:
Healthcare Integration
The integration of wearable technology with healthcare systems is revolutionizing patient care by enabling continuous health monitoring and real-time data sharing. Wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, collect a plethora of health metrics, including heart rate, blood pressure, glucose levels, and sleep patterns. This data can be seamlessly transmitted to healthcare providers, allowing for more informed clinical decisions and personalized treatment plans[1][2][3].
One significant benefit of this integration is the enhancement of remote patient monitoring. Patients with chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases can be monitored continuously, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits and enabling timely interventions. For example, AI-powered wearables can detect anomalies in health metrics and alert both patients and healthcare providers, facilitating early intervention and potentially preventing severe health events[1][2][3].
Moreover, the use of open application programming interfaces (APIs) in wearable devices, such as the Apple Watch and Apple Health app, ensures that collected data can be easily integrated into electronic health records (EHRs). This integration provides a comprehensive view of a patient's health, beyond the limited snapshots obtained during clinical visits. It also supports the development of personalized health plans, as healthcare providers can access detailed and continuous health data to tailor recommendations and treatments to individual needs[1][2].
The integration of wearable technology in healthcare also supports care management under risk-based contracting models. These models, which focus on the economic benefits of preventing health issues rather than treating them after they occur, benefit from the continuous data provided by wearables. This data helps care managers and remote monitors to create and maintain good health habits among patients, leading to better health outcomes and reduced healthcare costs[1].
Despite these advancements, several challenges must be addressed to fully realize the potential of healthcare integration with wearable technology. Data privacy and security are paramount concerns, as wearable devices collect sensitive health information that must be protected from unauthorized access. Additionally, the accuracy and reliability of data collected by consumer-grade wearables can vary, posing a challenge for clinical decision-making. Ensuring the accuracy of these devices and addressing usability issues, particularly for older users, are critical steps toward broader adoption and effectiveness[1][2][3].
In conclusion, the integration of wearable technology with healthcare systems offers significant benefits, including enhanced remote patient monitoring, personalized treatment plans, and improved health outcomes. However, addressing challenges related to data privacy, accuracy, and usability is essential to fully leverage the potential of this technology in transforming healthcare delivery[1][2][3][4].
Sources:
Future and Challenges
The future of wearable health technology is poised for remarkable advancements, driven by continuous innovation in sensor technology, artificial intelligence (AI), and data analytics. Emerging trends indicate that wearable devices will become even more integral to personal health management and clinical care.
One significant future development is the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and kinetic energy, into wearable devices. This innovation aims to enhance battery life and device sustainability, allowing for continuous health monitoring without frequent recharging interruptions[1][2]. Additionally, smart clothing embedded with sensors is expected to become more prevalent, offering new ways to monitor health metrics such as heart rate, muscle activity, and even hydration levels[3][4].
Augmented reality (AR) glasses represent another promising frontier. These devices will overlay digital information onto the real world, providing real-time feedback on physical activities and health metrics. This technology could be particularly useful in healthcare settings, offering applications ranging from surgical assistance to patient education[3][4].
Despite these exciting advancements, several challenges must be addressed to fully realize the potential of wearable health technology. Data privacy and security remain paramount concerns, as wearable devices collect sensitive health information that must be protected from unauthorized access[1][2][3]. Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data collected by these devices is also critical, as variations in sensor performance can impact clinical decision-making and patient outcomes[1][2][3].
Usability issues, particularly for older users, present another challenge. Devices must be designed with user-friendly interfaces, clear instructions, and comfortable wearability to ensure broad adoption and effectiveness[1]. Additionally, the digital divide poses a barrier to access, as not all populations have equal access to the latest wearable technologies and the internet connectivity required to use them effectively[6].
In conclusion, while the future of wearable health technology holds immense promise, addressing challenges related to data privacy, accuracy, usability, and accessibility is essential. By overcoming these obstacles, wearable devices can significantly enhance personal health management and transform healthcare delivery, making proactive and personalized care more attainable for everyone[1][2][3][4][6].
Sources:












Member discussion