In the quest for better health, weight management, and improved mental well-being, an ancient practice is gaining renewed attention: fermentation. This simple yet powerful food preparation technique offers a myriad of benefits that extend far beyond basic nutrition. Let's explore how incorporating fermented foods into your diet can be a game-changer for your overall health.
Understanding Fermentation
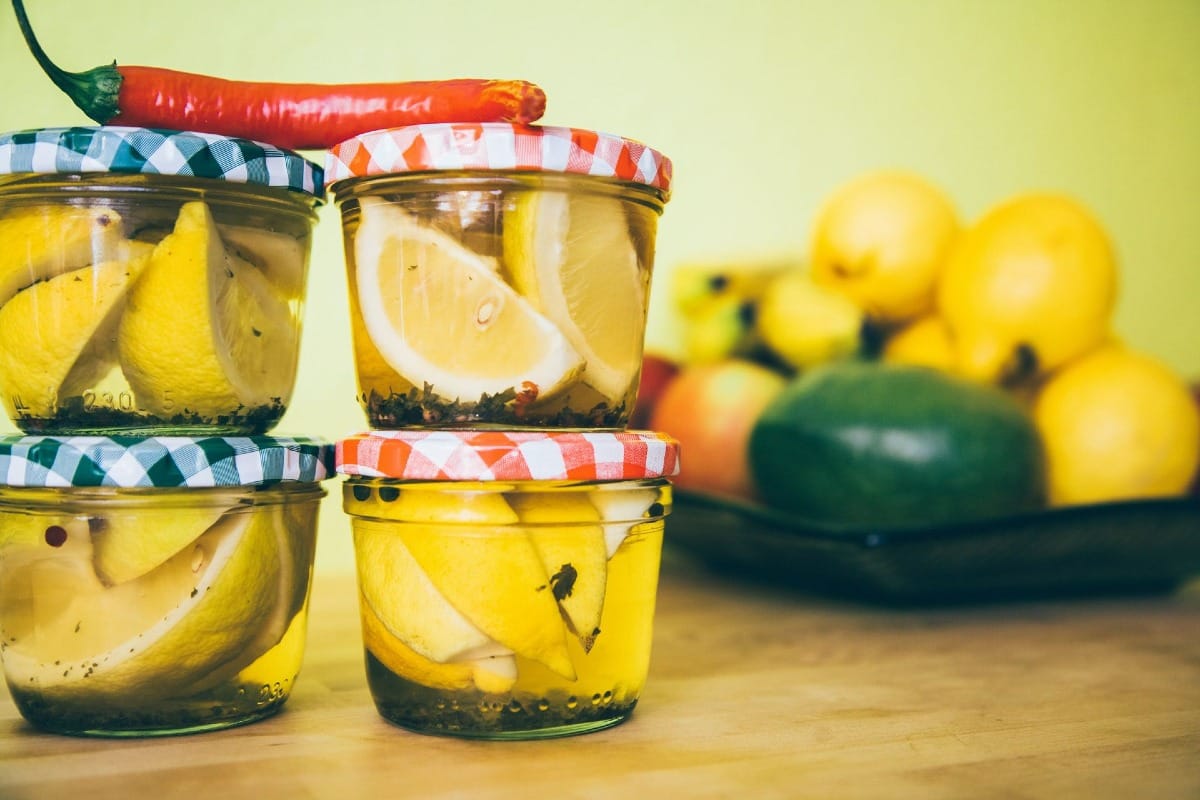
Fermentation is a metabolic process in which microorganisms like bacteria or yeast break down carbohydrates in food, producing beneficial compounds and altering the food's taste, texture, and nutritional profile. This process has been used for thousands of years to preserve food and enhance its flavors[2].
Types of Fermented Foods Some popular fermented foods include:
- Sauerkraut
- Kimchi
- Kombucha
- Kefir
- Yogurt
- Miso
- Tempeh
- Pickles
Each of these foods undergoes a unique fermentation process, resulting in distinct flavors and health benefits.
The Gut-Brain Connection
The relationship between our gut and brain, often referred to as the "gut-brain axis," plays a crucial role in our overall health. The gut is sometimes called our "second brain" due to its significant impact on our mental and emotional well-being[2].
How Gut Health Affects Mental Health Research has shown that poor gut health can be linked to various mental health issues, including:
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Mood swings
- Cognitive function
By improving gut health through fermented foods, we may positively influence our mental state and emotional resilience.
Weight Management and Fermented Foods
Fermented foods can be a valuable ally in weight management efforts. Here's how they contribute to maintaining a healthy weight:
- Improved Digestion Fermented foods are rich in probiotics, which help improve digestion and nutrient absorption. Better digestion can lead to more efficient metabolism and potentially aid in weight loss.
- Reduced Inflammation Chronic inflammation is often associated with obesity. Fermented foods have anti-inflammatory properties that may help combat this issue.
- Appetite Regulation Some studies suggest that probiotics found in fermented foods may help regulate appetite and reduce cravings, making it easier to maintain a healthy diet.
The Microbiome Diet
Professor Tim Spector, a leading expert in microbiome research, recommends consuming at least 30 different types of plants each week and incorporating fermented foods into our diets[2]. This approach, known as the microbiome diet, aims to nurture a diverse and healthy gut microbiome.
Benefits of a Diverse Microbiome A diverse microbiome has been associated with:
- Improved immune function
- Better weight management
- Reduced risk of chronic diseases
- Enhanced mental health
By following the microbiome diet and including fermented foods, we can support our gut health and potentially experience these benefits.
The Science Behind Fermented Foods
Several scientific studies have highlighted the positive effects of fermented foods on health. A Stanford University study found that a diet rich in fermented foods can increase immunity and overall health, aiding in weight maintenance and reducing the risk of cancer and cardiovascular disease[2].
Key Findings The study revealed that fermented foods can:
- Boost the immune system
- Improve overall health markers
- Support weight management
- Potentially reduce cancer risk
- Promote cardiovascular health
These findings underscore the importance of incorporating fermented foods into our daily diet.
DIY Fermentation: A Cost-Effective Approach
While commercially available fermented products can be expensive, making your own fermented foods at home is a cost-effective alternative. Not only does it save money, but it also allows you to control the ingredients and fermentation process.
Simple Fermentation Techniques
- Sauerkraut: Chop cabbage, massage with salt, and let it ferment in a jar for 2-6 weeks.
- Water Kefir: Feed kefir grains with sugar water and let ferment for 24-48 hours.
- Kombucha: Brew sweetened tea, add a SCOBY (Symbiotic Culture of Bacteria and Yeast), and ferment for 7-10 days.
These simple techniques can help you incorporate fermented foods into your diet without breaking the bank.
The Cultural Significance of Fermentation
Fermentation is not just a health trend; it's a practice deeply rooted in various cultures around the world. From Korean kimchi to German sauerkraut, fermented foods have been staples in traditional diets for centuries.
Global Fermentation Practices
- In Taiwan, preserved foods are an integral part of the cuisine.
- Balkan countries often ferment whole cabbage heads with added spices.
- Many cultures use fermentation as a method of food preservation during harsh seasons.
By exploring fermentation, we can connect with diverse culinary traditions and gain a deeper appreciation for the role of these foods in different cultures.
Incorporating Fermented Foods into Your Diet
Adding fermented foods to your daily meals doesn't have to be complicated. Here are some simple ways to increase your intake:
- Start your day with a small serving of yogurt or kefir.
- Add sauerkraut or kimchi as a side dish to your lunch or dinner.
- Use miso paste in soups or as a marinade for meats and vegetables.
- Enjoy kombucha as a refreshing afternoon drink.
- Experiment with tempeh as a protein source in your meals.
Remember, consistency is key. Aim to include at least one serving of fermented foods in your diet daily for optimal benefits.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While fermented foods offer numerous health benefits, it's essential to be aware of potential risks and considerations:
- Histamine Sensitivity Some fermented foods are high in histamines, which can cause reactions in sensitive individuals.
- Salt Content Many fermented foods are high in sodium, which may be a concern for those with high blood pressure or heart conditions.
- Interactions with Medications Certain fermented foods may interact with medications. Always consult with a healthcare provider before making significant changes to your diet.
The Future of Fermentation in Health and Wellness
As research continues to unveil the benefits of fermented foods, we can expect to see more emphasis on these products in the health and wellness industry. From personalized probiotics to innovative fermented food products, the future looks promising for this ancient practice.
Emerging Trends
- Precision probiotics tailored to individual microbiomes
- Fermented plant-based proteins for sustainable nutrition
- Integration of fermented foods in mental health treatment plans
By staying informed about these developments, we can make educated choices about incorporating fermented foods into our lifestyles for optimal health.
In conclusion, the simple act of adding fermented foods to our diet can have profound effects on our weight, mental health, and overall well-being. By nurturing our gut microbiome through fermentation, we're not just improving our physical health but potentially enhancing our mental and emotional resilience as well. Whether you choose to purchase fermented products or embark on your own fermentation journey at home, this ancient practice offers a natural and effective way to support your health goals.
Citations:
[1] https://www.independent.co.uk/health-and-fitness/gut-health-weight-loss-mental-health-b2588894.html












Member discussion